S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Diversity, Equity, & Inclusion
Investor Relations
Featured Products
Ratings & Benchmarks
By Topic
Market Insights
About S&P Global
Corporate Responsibility
Diversity, Equity, & Inclusion
Investor Relations
S&P Global Offerings
Featured Topics
Featured Products
Events
Language
S&P Global — 14 Sep, 2023 — Global
By S&P Global
Start every business day with our analyses of the most pressing developments affecting markets today, alongside a curated selection of our latest and most important insights on the global economy.
It’s a Whole New LNG Market
Liquefied natural gas exists to solve a problem. Many places use natural gas, but not all of those places have sufficient reserves to meet their consumption needs. When oceans or mountain ranges make natural gas pipelines impractical, the solution is to send natural gas by tankers. However, because natural gas is a vapor, transporting it aboard ships in large volumes is not feasible. LNG allows natural gas exporters to solve the problem by cooling natural gas to minus 260 degrees F, turning the natural gas into a liquid, which is easier to transport and store in cryogenic tanks. When the LNG cargo arrives at its destination, the liquid is pumped to a regasification facility, where it is converted back to a gas for consumption. For over a decade, many Asian economies have been net importers of LNG from countries such as Australia, Qatar and the US, which collectively account for about 60% of global LNG supply. Following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and the reduction in Russian natural gas flows to Europe, the sudden European demand for LNG is transforming the market.
Historically, Europe was just a place for exporters to dump LNG cargoes when they couldn’t get a better price in Asia. That dynamic changed in 2022. In 2021, Europe relied on Russia for 40% of its gas demand, and European LNG infrastructure was not sufficient to compensate for the loss of Russian gas. But Europe has begun to expand its LNG processing infrastructure and regasification capacity faster than expected. For example, Germany had no LNG import capability before the invasion of Ukraine, but it has since established three floating storage regasification units.
"Europe has achieved its target of 90% storage capacity ahead of winter,” Petronet LNG Managing Director and CEO Akshay Kumar Singh told S&P Global Commodity Insights. “Unless there is an extreme winter in Europe and concurrent LNG supply disruptions, we expect prices to be comparable to the winter prices witnessed in the years before the volatility seen in the last two years."
The sudden increase in European LNG demand and regasification facilities has transformed the way the markets function and price cargoes. European gas markets used to price LNG at a similar outright value to local natural gas hubs. However, in the overheated natural gas markets of 2022, these prices started to diverge. Now, buyers prefer to price LNG at the cargo price, which is more likely to reflect the current market dynamic at the time of delivery rather than the average across the month. This is increasingly making cargoes the base load for Europe’s market.
Continued European demand and a recovery in demand from Asia are likely to drive LNG prices for the next couple of years. Since infrastructure for LNG — both liquefaction and regasification facilities — can take years to build out, S&P Global Ratings expects the global spot market for LNG to remain tight through 2025–2026. Following 2026, many planned facilities will come online just as global LNG demand could begin to slow due to global decarbonization efforts. This may mean that the LNG market temporarily becomes oversupplied, leading to a fall in global gas prices.
Today is Thursday, September 14, 2023, and here is today’s essential intelligence.
Written by Nathan Hunt.
Default, Transition And Recovery: Corporate Defaults Record Highest August Total Since 2009
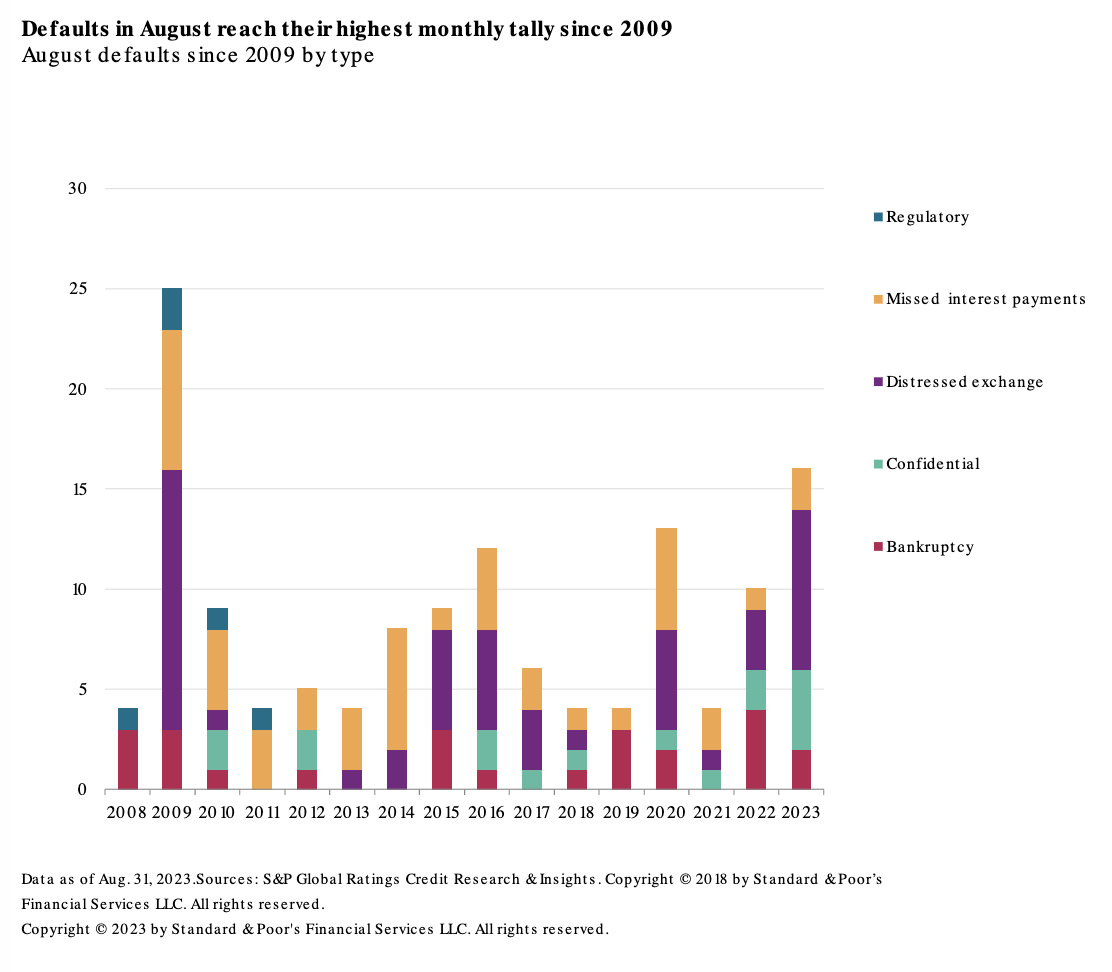
Historically, default counts tend to slow in the summer, specifically in August where the 10-year monthly average is 8.6 defaults, compared with an overall monthly 10-year average of 9.8 defaults. However, with 16 defaults, this August's tally was the highest August monthly tally since 2009 during the Global Financial Crisis.
—Read the report from S&P Global Ratings
Access more insights on the global economy >
Innovating For Insurance: S&P 500 Duo Swift Index
How is intraday volatility rebalancing helping new multi-asset indices rapidly respond to changing markets? Look inside the S&P 500 Duo Swift Index, a diverse, multi-asset, risk-controlled index that is dynamic by design.
—Watch the video from S&P Dow Jones Indices
Access more insights on capital markets >
Is The Russian-Ukrainian Conflict Accelerating The Arms Race? Arms Trade Analysis
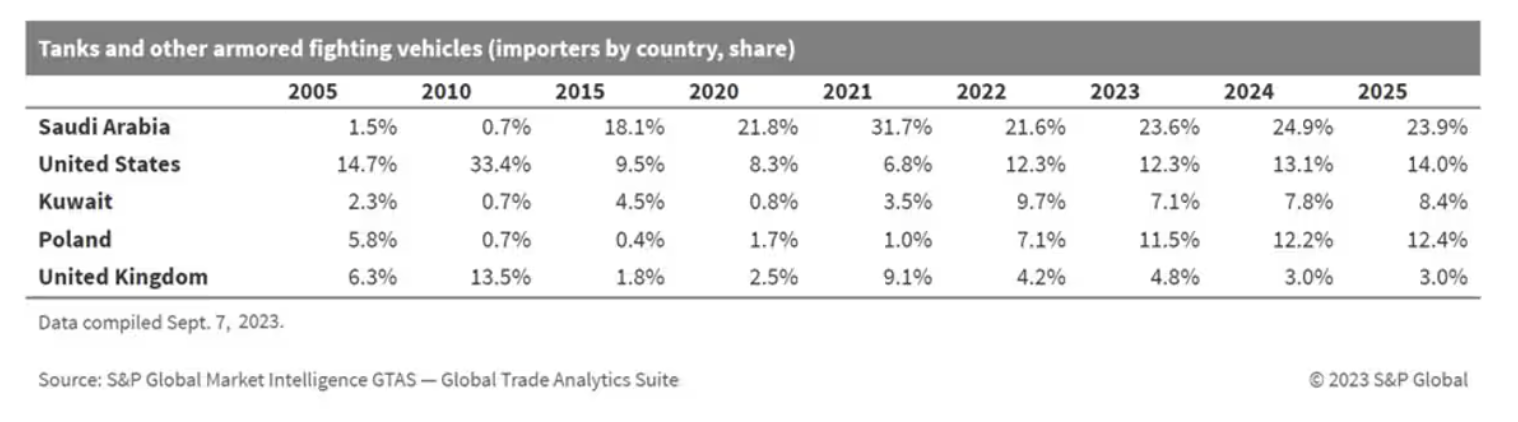
Developments for 2022 were the driving force of change in many areas of global trade with particular influence on global and especially European armaments. The aim of this analysis is to make an assessment on trends and developments in armaments trade in recent years. It is worth noting that this analysis applies only to nonconfidential reported trade data and does not cover secret arms purchases. It should also be noted that exports should not be confused with total armaments production, as armaments industry supplies mainly domestic demand.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence
Access more insights on global trade >
As Companies Prepare To Implement New International Climate Standard, Disclosure Varies Widely Around The World
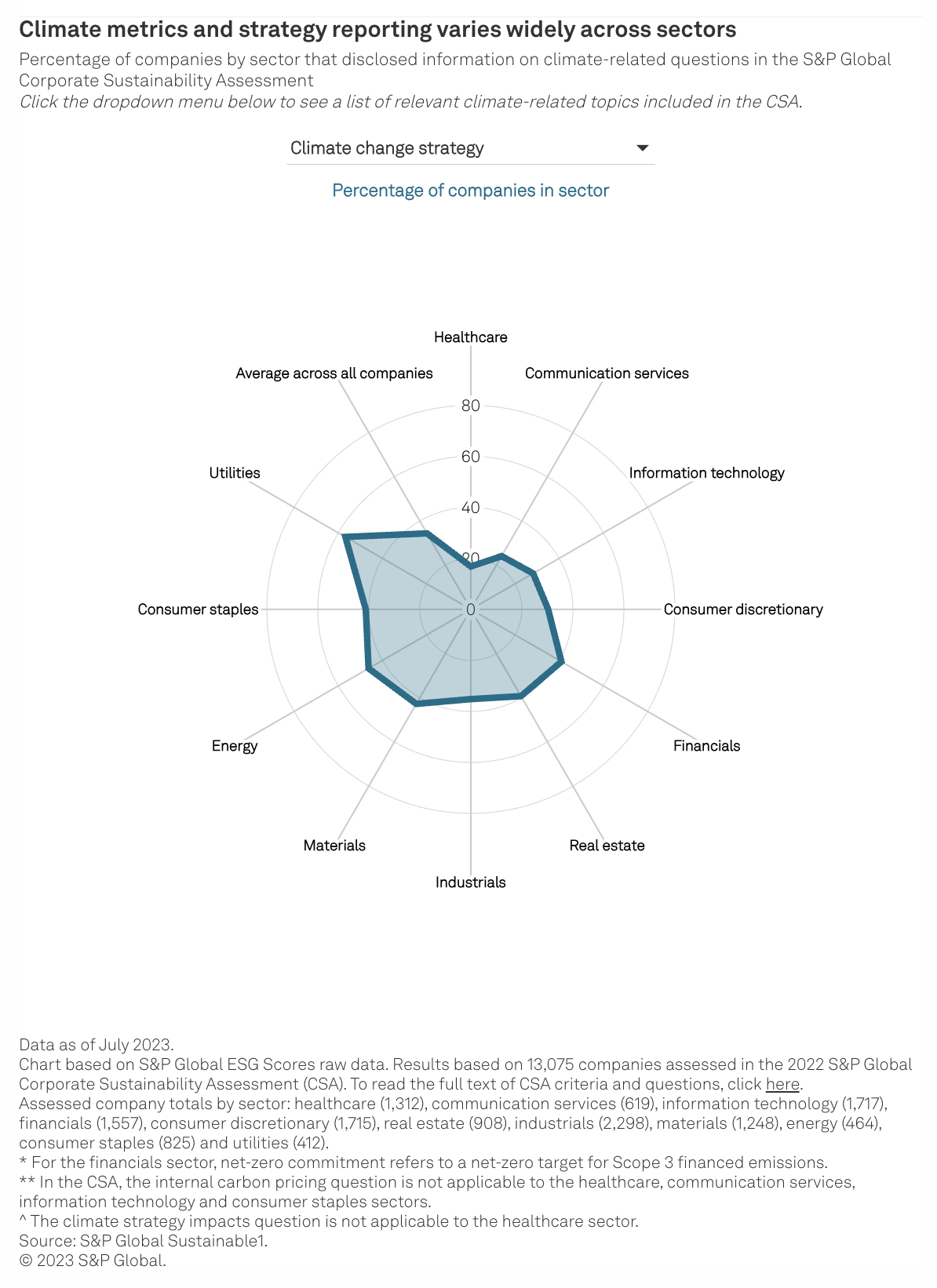
A new climate disclosure standard from the International Sustainability Standards Board asks companies to disclose climate-related information and metrics. The IFRS S2 Climate-related Disclosures standard could become the basis for globally consistent climate disclosure if it is widely adopted. As companies prepare to implement S2, S&P Global Sustainable1 used S&P Global Corporate Sustainability Assessment data to understand the widely varying levels of climate disclosure around the world.
—Read the article from S&P Global Sustainable1
Access more insights on sustainability >
Oil Product Stockpiles Rebound From 17-Month Low
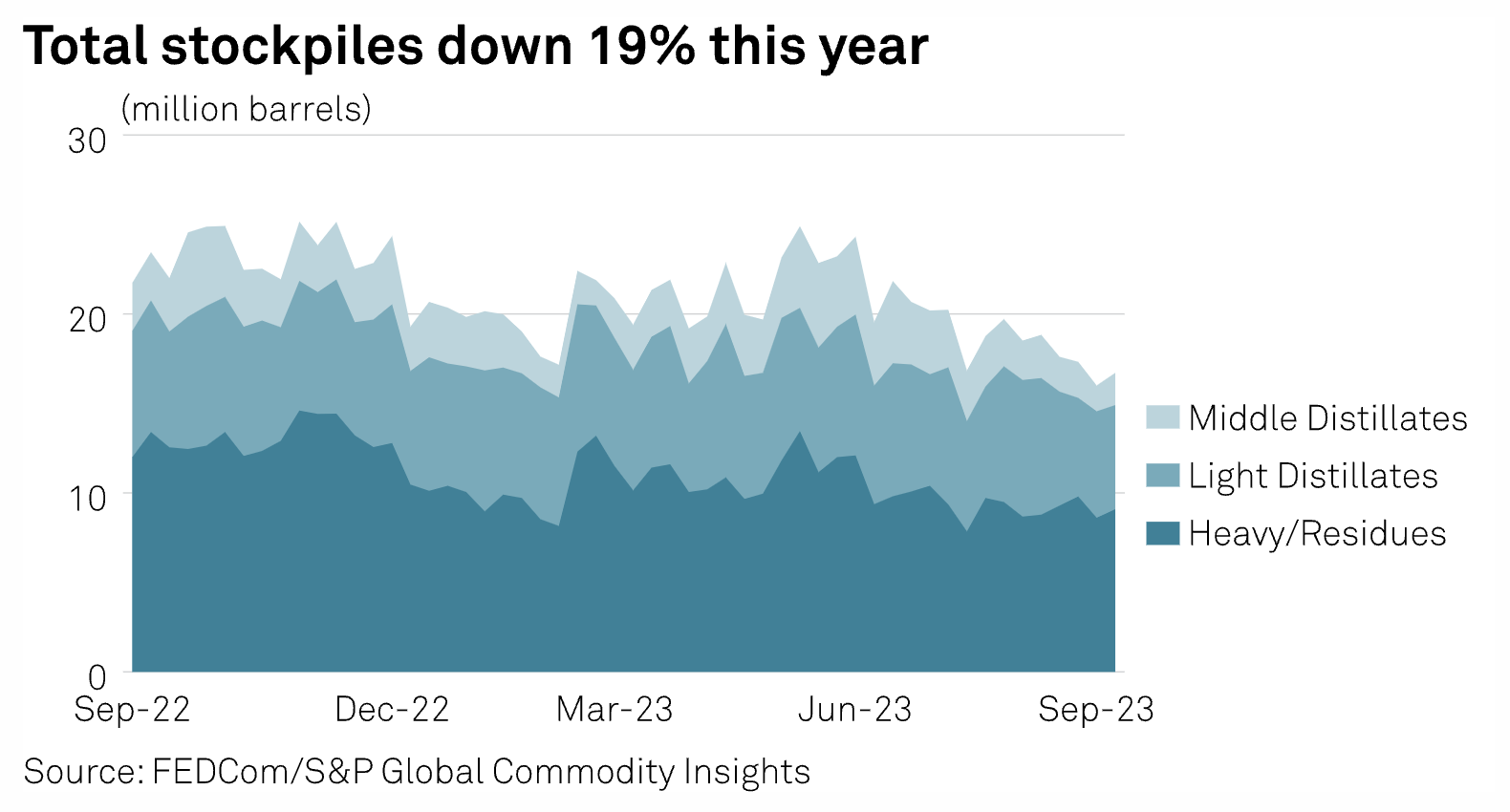
Stockpiles of oil products at the UAE's Port of Fujairah climbed 4.5% in the week ended Sept. 11, the first increase in four weeks from a 17-month low a week earlier, according to latest data from the Fujairah Oil Industry Zone. Total inventories rose to 16.717 million barrels as of Sept. 11, after falling to its lowest since April 2022 on Sept. 4, the FOIZ data provided exclusively on Sept. 13 to S&P Global Commodity Insights showed. The total stockpile dropped 15% in the previous four weeks and was down 19% since the end of 2022.
—Read the article from S&P Global Commodity Insights
Access more insights on energy and commodities >
Assessing Usage Of Streaming Services By Charter Pay TV Subs
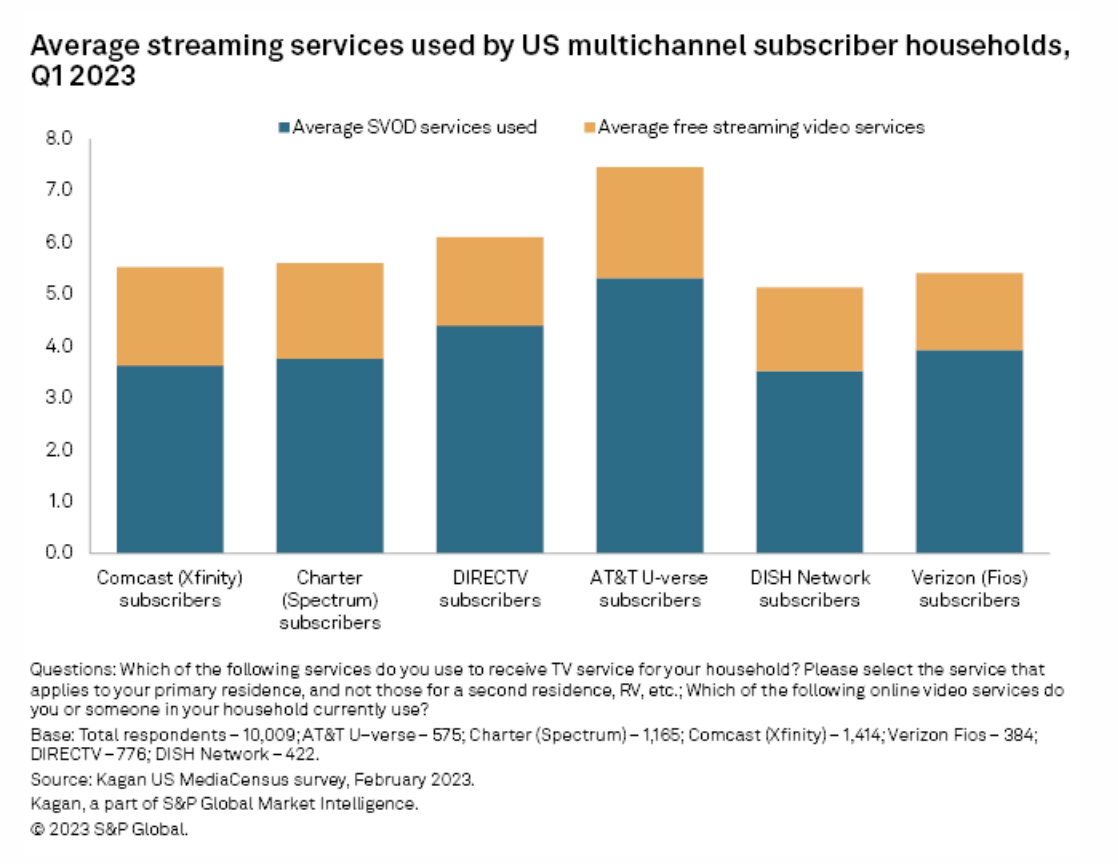
While the rise of streaming alternatives has played a key role in the wave of cord cutting roiling the traditional multichannel TV industry in the US, pay TV households tend to be heavy users of subscription video-on-demand services as well as free video streaming offerings. As traditional TV network owners Comcast Corp., Walt Disney Co., Paramount Global and Warner Bros. Discovery Inc. shift programming to streaming services such as Peacock, Disney+, ESPN+, Hulu, Max, Peacock, Paramount+, Max and Discovery+, some pay TV households may effectively be "paying twice" for the same programming depending on pay TV package, what streaming services households subscribe to and what programming they typically view.
—Read the article from S&P Global Market Intelligence

